graph with polarimeter values for reaction rate|example of measuring reaction rate : manufacturer One method of using graphs to determine reaction order is to use relative rate information. Plotting the log of the relative rate versus log of relative concentration provides information about the reaction. MG - Clima e previsão do tempo: Meteorologia é na Climate.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webView 199 NSFW pictures and videos and enjoy SunnyrayNSFW with the endless random gallery on Scrolller.com. Go on to discover millions of awesome videos and pictures in .
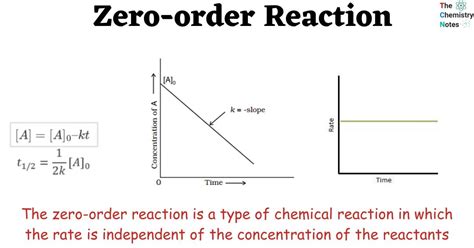
zero order reaction graphs
One method of using graphs to determine reaction order is to use relative rate information. Plotting the log of the relative rate versus log of relative concentration provides information about the reaction. A measure of the rate of the reaction at any point is found by measuring the slope of the graph. The steeper the slope, the faster the rate. Because the initial rate is important, the .In order to determine the rate law for a reaction from a set of data consisting of concentration (or the values of some function of concentration) versus time, make three graphs. The graph that .
To use graphs to analyze the kinetics of a reaction. In Section 14.3 "Methods of Determining Reaction Order", you learned that the integrated rate law for each common type of reaction (zeroth, first, or second order in a single reactant) .
ABSTRACT . You will be using a Vernier Go Direct Polarimeter with a 589 nm light source to measure the angle of rotation of polarized light passing through solutions of sucrose in water. .
Polarimeter Most physical properties of enantiomers i.e., melting point, boiling point, refractive index, etc. are identical. However, they differ in a property called optical activity, in which a sample rotates the plane of polarization of a .The mean rate of a chemical reaction is different to the instantaneous rate that changes throughout the reaction. Graphs of mass, volume, or concentration vs. time can all represent .Graphical Methods for Determining Reaction Order—A Summary. We have just seen that first-, second-, and zero-order reactions all have unique, integrated rate-law equations that allow us to plot them as a straight line (y = mx + b) (Table .
In order to study the factors that change the speed of a reaction, we must first develop an understanding of how the rate of reaction is monitored during a reaction. 1. The graph in .
Graph the data as concentration versus t, ln concentration versus t, and 1/concentration versus t. Then determine the reaction order in C 4 H 6, the rate law, and the rate constant for the reaction.This notation means that the measurement was conducted at 25 o C using the D-line of the sodium lamp (λ=589.3 nm). A sample containing 1.00 g/mL of the compound in a 1 dm tube exhibits an optical rotation of 3.5 o in clockwise direction. Note that the instrument used in Chem 30BL and Chem 30CL can provide the specific optical rotation, which already corrects the .
The gradient of a rate of reaction graph can be calculated from a tangent drawn at a point on the curve. Common misconception. To calculate the instantaneous rate of reaction by reading values from the graph at a specific time. The rate constant (k) of the first-order kinetics helps to understand how the rate of reaction is affected by the concentration of sucrose. It is found to be 1.23x 10 −2 ± 0.05 min −1 M −1 . The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by NICE CXone Expert and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant . For example, the reaction rates of many reactions that occur at room temperature approximately double with a temperature increase of only 10°C. In this section, we will use the collision model to analyze this relationship between temperature and reaction rates.
As the reaction reached completion, the angle of rotation for plane polarized light slowly inverted from 6° to -2°. Treatment of this data generated two distinct plots, with slope values equal in magnitude to the rate constant of the pseudo-first order reaction rate.Solution. A Because O 2 has the smallest coefficient in the balanced chemical equation for the reaction, define the reaction rate as the rate of change in the concentration of O 2 and write that expression.. B The balanced chemical equation shows that 2 mol of N 2 O 5 must decompose for each 1 mol of O 2 produced and that 4 mol of NO 2 are produced for every 1 mol of O 2 .
how to measure temperature reaction
The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample. In summary: \[[\alpha] = \frac{\alpha}{c \times l} \nonumber\] a is the measured optical rotation. c is the sample concentration in grams per deciliter (1 dL = 10 mL). The reaction rate of the single stage, hydrogen ion catalyzed hydrolysis of sucrose into fru ctose and glucose in aqueous Optical Rotation Measurement with a Novel Polarimeter Chem. Educator, Vol .The reaction of sucrose with HCl follows first order reaction. Find the rate constant of the given reaction. . In a 1st order reaction A → products, the concentration of the reactant decreases to 6.25 % of its initial value in 80 minutes. What is (i) the rate constant and (ii) the rate of reaction, 100 minutes after the start, if the .Answer: 1.Identify the values on the graph. In this question, we need to calculate the rate of reaction at a certain point during the reaction.
Two factors can be controlled in the experiment and must be accounted for when comparing an experimental result to a reported value. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): The effect of concentration on optical rotation. The more concentrated the sample (the more molecules per unit volume), the more molecules will be encountered.
Given: balanced chemical equation, reaction times, and concentrations Asked for: graph of data, rate law, and rate constant Strategy: A Use the data in the table to separately plot concentration, the natural logarithm of the concentration, and the reciprocal of the concentration (the vertical axis) versus time (the horizontal axis). Compare the graphs with those in Figure .it intersects the Y-axis is the value of intrinsic rotation Intrinsic rotation 0 x-axis y-axis Concentration of solution 6SHFL¿F URWDWLRQ Fig. 12.2: Graph shows determination of intrinsic rotation. Table 12.1: 6SHFL¿F URWDWLRQ RI VRPH VXJDU LQ ZDWHU DW oC (showing dependence of VSHFL¿F URWDWLRQ RQ QDWXUH RI VXEVWDQFHIn this experiment, hydrochloric acid is used to catalyze the reaction while its rate is monitored using a polarimeter. The experiment will be repeated using the enzyme invertase to catalyze the reaction. . Calculate the specific rotation of .Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more.
The measured value in a polarimeter is the optical rotation, α [°OR]. From the optical rotation further values can be derived: . Rate this article. You have already rated this article. Table of contents 1. Definition of polarimetry 2. What .sample. Compare to the literature value. (10 points) Part II. 1. Enter your tabulated data from lab into an Excel sheet. Be sure to use the optical rotation determined in step 9 of Part I for 15 % w/v sucrose as your value at t = 0 min. (10 points) 2. Plot the angle of rotation vs time, and determine the rate constant for this reaction with respect
Initial rates of reaction were determined by following the production of glucose directly as a function of time over a wide range of substrate concentrations (0.04M to 2.06M). To calculate rate of reaction from a graph, the general formula change in concentration/change in time is used. To find the average rate, find the change in concentration/change in time from the .Determination of the rate at which sucrose hydrolyses by calculating its angle of optical rotation using a polarimeter at 25°C in 15 minute intervals for a period of ±100 minutes. . Graph: Calculation of rate constant: At 25°C . The role of this ion is to catalyse the reaction. H+ is 2 mol dm-3 at the start of the reaction. No this value .
initial rate: instantaneous rate of a chemical reaction at t = 0 s (immediately after the reaction has begun) instantaneous rate: rate of a chemical reaction at any instant in time, determined by the slope of the line tangential to a graph of concentration as a function of time
A rate law is an expression which relates that rate of a reaction to the rate constant and the concentrations of the reactants. A rate constant, \(k\), is a proportionality constant for a given reaction. The general rate law is usually expressed as: \[ \text{Rate} = k[A]^s[B]^t \label{2} \]
The measurements are carried out in a polarimeter, which essentially consists of a sodium lamp, a polarizer, a cuvette and an analyzer. . Reaction rate is definded as change in concentration per time. For the given reaction > @ > @ > @ t t d t d S d d F d . Linear regression of the graph gave the following results (for RGP evaluation, see .Either the differential rate law or the integrated rate law can be used to determine the reaction order from experimental data. Often, the exponents in the rate law are the positive integers: 1 and 2 or even 0. Thus the reactions are zeroth, first, or second order in each reactant.The common patterns used to identify the reaction order are described in this section, where we focus on . The instantaneous rate of a reaction is given by the slope of a tangent to the concentration-vs.-time curve. Three such rates have been identified in this plot. An instantaneous rate taken near the beginning of the reaction (t = 0) is known as an initial rate (label (1) here). As we shall soon see, initial rates play an important role in the . An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and a few wires, all held in place with plastic interlocking toy bricks, such as Lego bricks. The instrument was used to demonstrate the optical rotation of plane polarized light as .
webQueen’s University Industrial Relations Centre (IRC) is a leading provider of premium professional development programs in labour relations, human resources and organization development. IRC programs are designed for busy practitioners, delivered by subject matter experts, and grounded in adult learning principles.
graph with polarimeter values for reaction rate|example of measuring reaction rate